

#Efficiency #Heat Pumps #Heating and Cooling #reduce #Sustainable Buildings #Sustainable Home
Doug Fogelson
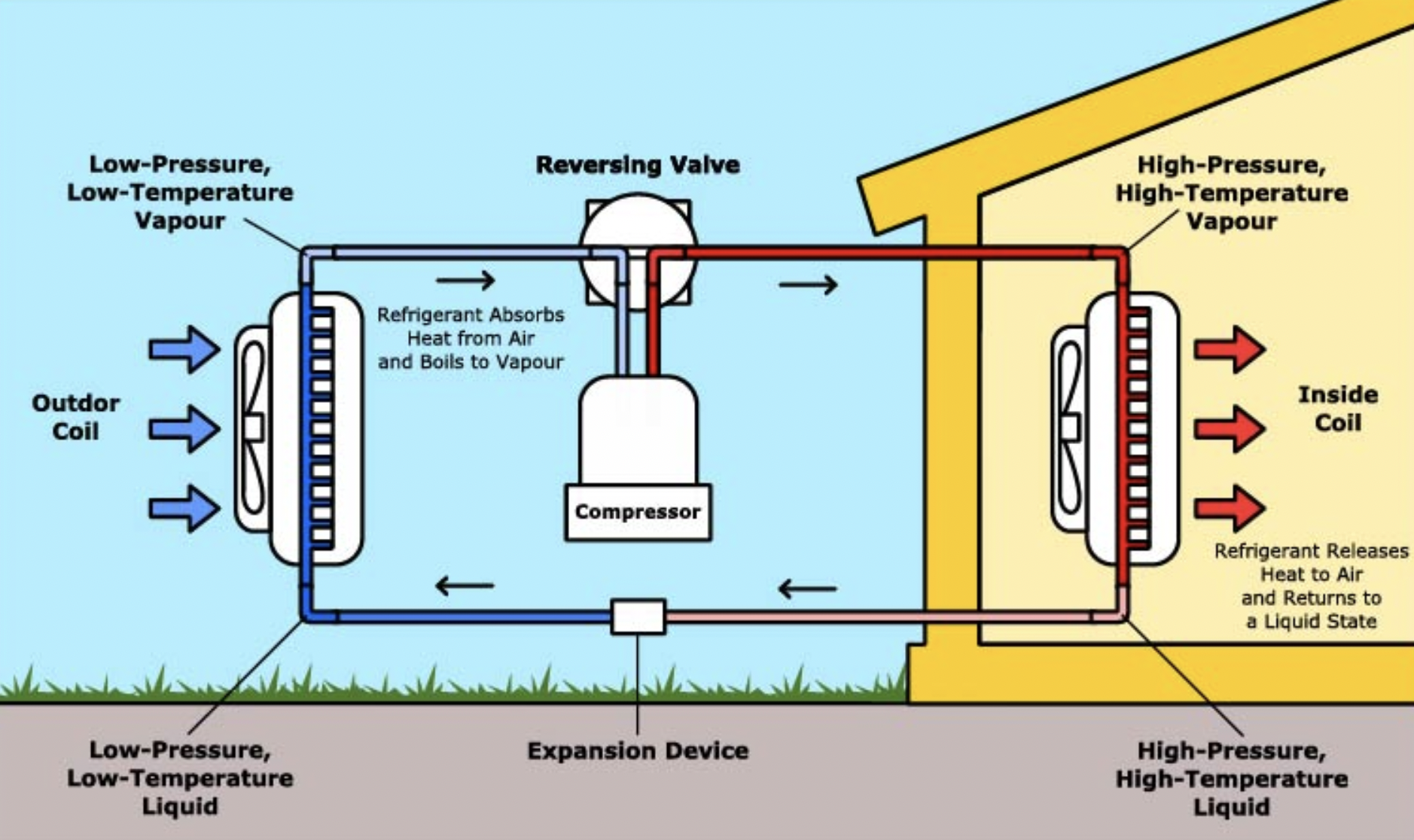
You may have heard of this solution as an energy efficient alternative to gas furnace heating and/or typical air conditioning systems, but what is a “heat pump”? Heat pump systems use a refrigerant to stimulate “work” in the exchange between outside to inside air temperatures or vice versa. When it is cold outside the refrigerant changes from a gas to a liquid, emitting heat when doing so, and when warm outside it can change states in reverse from a liquid to a gas and cool things down.
Pulling air between an “exchanger” inside a building to one outside the building (and vice versa) is how an “Air Source” heat pump works, but there are other versions that can work by pumping/exchanging air between a home and the cooler ground, underground, or water in areas nearby.
Using a heat pump system can reduce emissions by an average somewhere between 45-90% depending on a few variables. Powering heat pumps by renewable sources such a solar or wind makes this an even better option to consider in the transition to lower overall impact on the environment.
It is important to note that a well weatherized home will have an easier time heating and cooling, with less leaks and more insulation, so that the heating/cooling system won’t have to work extra hard.
Heat pumps are three times less efficient than those that burn fossil fuels.